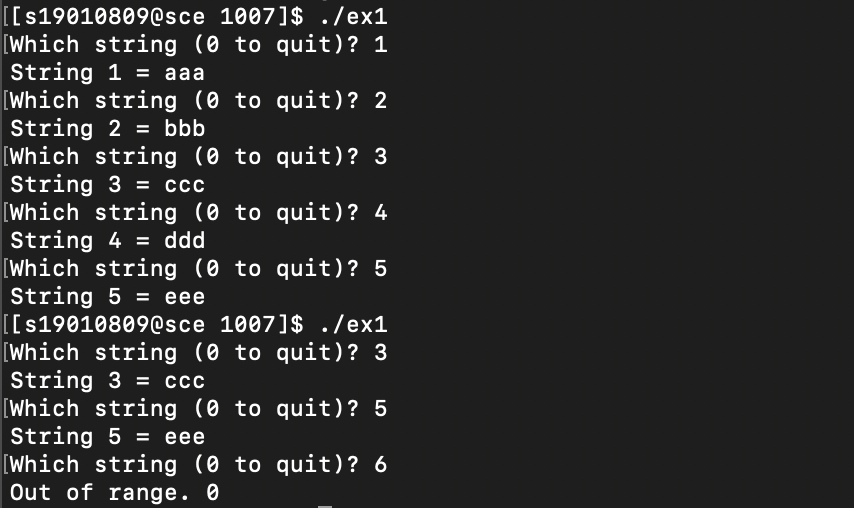
ex1. 고수준 입출력함수를 사용하여 5개의 스트링을 받아들여 파일에 저장한 후, 화면으로 스트링 번호를 입력하면 파일에서 해당 스트링을 읽어 화면에 출력하는 부분을 for문을 사용하여 작성하라
data file(testdata) : aaabbbcccdddeee
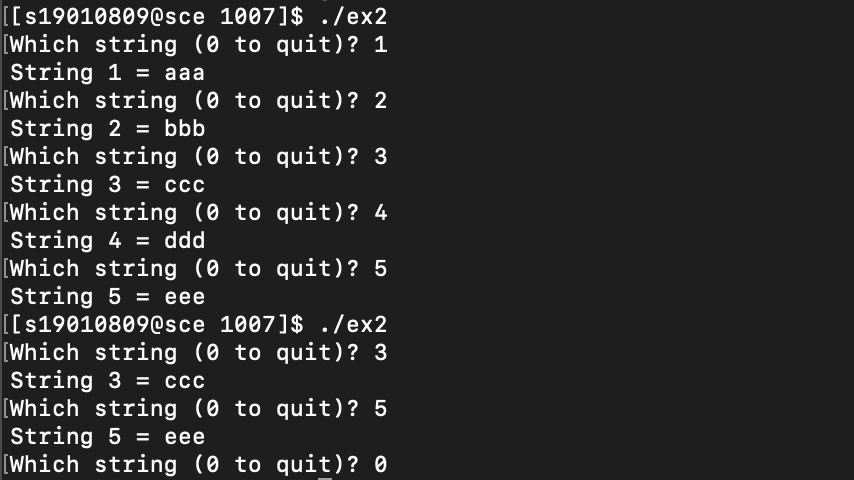
$ ./test
1
aaa
3
ccc
4
ddd
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <errno.h>
#define NSTRINGS 5
#define STRSIZE 3
char* strings[] = {"aaa", "bbb", "ccc", "ddd", "eee"};
int main(int argc, char* argv[]) {
int i, n;
FILE* fp;
char buf[STRSIZE], template[32];
if ((fp = fopen("testdata", "w+")) == NULL) {
exit(1);
}
for (n = 0; n < NSTRINGS; n++) {
fwrite(strings[n], sizeof(char), STRSIZE, fp);
}
for (i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
printf("Which string (0 to quit)? ");
scanf("%d", &n);
if (n == 0) {
fclose (fp);
exit(0);
}
if (n < 0 || n > NSTRINGS) {
fclose(fp);
fprintf(stderr, "Out of range. %d\n", errno);
exit(1);
}
fseek(fp, (n - 1) * STRSIZE, SEEK_SET);
fread(buf, sizeof(char), STRSIZE, fp);
printf("String %d = %s\n\n", n, buf);
}
fclose(fp);
exit(0);
return 0;
}
ex2. ex1의 프로그램을 시스템 콜로 변환하여 작성하라
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#define NSTRINGS 5
#define STRSIZE 3
char* strings[] = {"aaa", "bbb", "ccc", "ddd", "eee"};
int main(int argc, char* argv[]) {
int i, n;
//FILE* fp;
int fd;
char buf[STRSIZE];
/*
if ((fp = fopen("testfile", "w+")) == NULL) {
exit(1);
}
*/
fd = open("testdata", O_RDWR|O_CREAT, 0644);
/*
for (n = 0; n < NSTRINGS; n++) {
fwrite(strings[n], sizeof(char), STRSIZE, fp);
}
*/
for (n = 0; n < NSTRINGS; n++) {
write(fd, strings[n], STRSIZE * sizeof(char));
}
for (i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
printf("Which string (0 to quit)? ");
scanf("%d", &n);
if (n == 0) {
// fclose (fp);
close(fd);
exit(0);
}
if (n < 0 || n > NSTRINGS) {
close(fd);
fprintf(stderr, "Out of range.\n");
exit(1);
}
// fseek(fp, (n - 1) * STRSIZE, SEEK_SET);
// fread(buf, sizeof(char), STRSIZE, fp);
memset(buf, 0, sizeof(buf));
lseek(fd, (off_t)(n - 1) * STRSIZE, SEEK_SET);
read(fd, buf, STRSIZE * sizeof(char));
buf[STRSIZE] = '\0';
printf("String %d = %s\n", n, buf);
}
//fclose(fp);
close(fd);
exit(0);
return 0;
}
참고 및 출처: 시스템 프로그래밍 리눅스&유닉스(이종원)
'Computer Science > UNIX & Linux' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [UNIX/Linux] ep6) 프로세스 정보 (4) | 2024.10.12 |
|---|---|
| [UNIX/Linux] ep5) 시스템 정보 (1) | 2024.10.10 |
| [UNIX/Linux] ep4) 고수준 파일 입출력 (1) | 2024.10.07 |
| [UNIX/Linux] ep3+) 저수준 파일 입출력 함수 실습 (4) | 2024.10.02 |
| [UNIX/Linux] ep3) 저수준 파일 입출력 (5) | 2024.09.30 |



