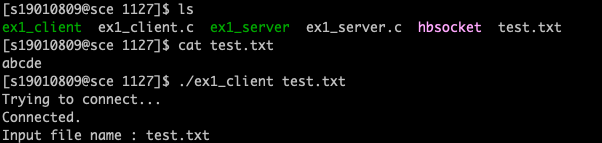
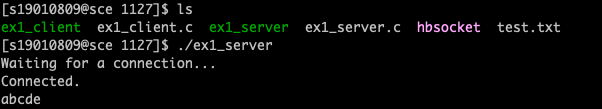
ex1. 같은 시스템에서 클라이언트가 명령행 인자로 파일 이름을 받은 후 이를 서버로 보낸다. 서버는 파일 이름을 받아 파일 내용을 화면에 출력하는 프로그램을 작성하라
(ex1_client.c)
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <sys/un.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#define SOCK_PATH "hbsocket"
int main(int argc, char* argv[]) {
int s, t, len, i;
struct sockaddr_un remote;
if ((s = socket(AF_UNIX, SOCK_STREAM, 0)) == -1) {
perror("socket");
exit(1);
}
printf("Trying to connect...\n");
remote.sun_family = AF_UNIX;
strcpy(remote.sun_path, SOCK_PATH);
len = strlen(remote.sun_path) + sizeof(remote.sun_family);
if (connect(s, (struct sockaddr*)&remote, len) == -1) {
perror("connect");
exit(1);
}
printf("Connected.\n");
printf("Input file name : %s\n", argv[1]);
if (send(s, argv[1], strlen(argv[1]) + 1, 0) == -1) {
perror("send");
exit(1);
}
close(s);
return 0;
}
(ex1_server.c)
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <sys/un.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#define SOCK_PATH "hbsocket"
printFile(const char* fname) {
int rfd, n;
char buf[64];
rfd = open(fname, O_RDONLY);
if (rfd == -1) {
perror("Open ");
return 1;
}
while ((n = read(rfd, buf, 5)) > 0) {
if (write(1, buf, n) != n) {
perror("Write");
}
}
close(rfd);
}
int main(void) {
int s, s2, t, len, n, done;
struct sockaddr_un local, remote;
char str[64], filename[64];
if ((s = socket(AF_UNIX, SOCK_STREAM, 0)) == -1) {
perror("socket");
exit(1);
}
local.sun_family = AF_UNIX;
strcpy(local.sun_path, SOCK_PATH);
unlink(local.sun_path);
len = strlen(local.sun_path) + sizeof(local.sun_family);
if (bind(s, (struct sockaddr*)&local, len) == -1) {
perror("bind");
exit(1);
}
if (listen(s, 5) == -1) {
perror("listen");
exit(1);
}
printf("Waiting for a connection...\n");
t = sizeof(remote);
if ((s2 = accept(s, (struct sockaddr*)&remote, &t)) == -1) {
perror("accept");
exit(1);
}
printf("Connected.\n");
memset(str, sizeof(str), 0);
n = recv(s2, str, 64, 0);
if (n <= 0) {
if (n < 0) {
perror("recv");
}
}
printFile(str);
close(s2);
close(s);
return 0;
}
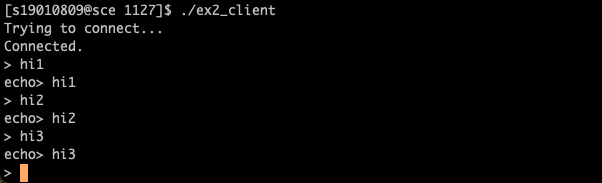
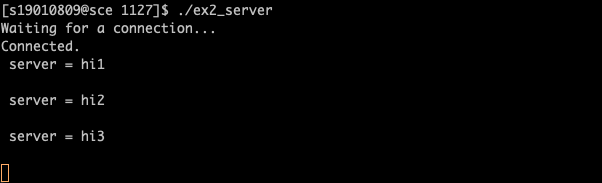
ex2. 두 개의 session을 열어서 AF_UNIX로 다음을 작성하라.
클라이언트에서 화면으로 입력받은 내용을 서버에서 받은 후, 다시 클라이언트에게 그대로 보낸다. 클라이언트는 받은 내용을 화면에 출력한다.
(ex2_client.c)
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <sys/un.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#define SOCK_PATH "hbsocket"
int main(void) {
int s, t, len, i;
struct sockaddr_un remote;
char str[100], rstr[100];
if ((s = socket(AF_UNIX, SOCK_STREAM, 0)) == -1) {
perror("socket");
exit(1);
}
printf("Trying to connect...\n");
remote.sun_family = AF_UNIX;
strcpy(remote.sun_path, SOCK_PATH);
len = strlen(remote.sun_path) + sizeof(remote.sun_family);
if (connect(s, (struct sockaddr*)&remote, len) == -1) {
perror("connect");
exit(1);
}
printf("Connected.\n");
while (printf("> "), fgets(str, 100, stdin), !feof(stdin)) {
if (send(s, str, strlen(str), 0) == -1) {
perror("send");
exit(1);
}
memset(str, '\0', 100);
memset(rstr, '\0', 100);
if ((t=recv(s, rstr, 100, 0)) > 0) {
rstr[t] = '\0';
printf("echo> %s", rstr);
}
}
close(s);
return 0;
}
(ex2_server.c)
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <sys/un.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#define SOCK_PATH "hbsocket"
int main(void) {
int s, s2, t, len, n, done;
struct sockaddr_un local, remote;
char str[100];
if ((s = socket(AF_UNIX, SOCK_STREAM, 0)) == -1) {
perror("socket");
exit(1);
}
local.sun_family = AF_UNIX;
strcpy(local.sun_path, SOCK_PATH);
unlink(local.sun_path);
len = strlen(local.sun_path) + sizeof(local.sun_family);
if (bind(s, (struct sockaddr*)&local, len) == -1) {
perror("bind");
exit(1);
}
if (listen(s, 5) == -1) {
perror("listen");
exit(1);
}
printf("Waiting for a connection...\n");
t = sizeof(remote);
if ((s2 = accept(s, (struct sockaddr*)&remote, &t)) == -1) {
perror("accept");
exit(1);
}
printf("Connected.\n");
done = 0;
do {
n = recv(s2, str, 100, 0);
if (n <= 0) {
if (n < 0) {
perror("recv");
}
done = 1;
}
if (!done)
if (send(s2, str, n, 0) < 0) {
perror("send");
done = 1;
}
printf(" server = %s\n", str);
} while (!done);
close(s2);
close(s);
return 0;
}
ex3. IP 주소를 입력받아 이에 해당하는 호스트 이름을 출력하는 프로그램을 작성하라
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <arpa/inet.h>
#include <netinet/in.h>
#include <netdb.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
int main() {
char ip[256];
in_addr_t addr;
struct hostent* hp;
struct in_addr in;
printf("Input IP Address: ");;
scanf("%s", ip);
if ((addr = inet_addr(ip)) == (in_addr_t)-1){
printf("Error: %s \n", ip);
exit (2);
}
hp = gethostbyaddr((char*)&addr, 4, AF_INET);
if (hp == NULL) {
printf("Host information not found\n");
exit (2);
}
(void)memcpy(&in.s_addr, *hp->h_addr_list, sizeof(in.s_addr));
printf("Name=%s IP=%s\n", hp->h_name, inet_ntoa(in));
return 0;
}
ex4. 클라이언트로부터 두 개의 정수를 받아 서버가 곱셈을 실행한 후, 답을 클라이언트에게 보낸다. 만약 답이 0이면 클라이언트와 서버가 모두 종료하는 프로그램을 작성하라
(ex4_client.c)
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <sys/un.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#define SOCK_PATH "hbsocket"
int main(void) {
int s, t, len, i;
struct sockaddr_un remote;
int *num, ans;
num = (int*)malloc(2 * sizeof(int));
if ((s = socket(AF_UNIX, SOCK_STREAM, 0)) == -1) {
perror("socket");
exit(1);
}
printf("Trying to connect...\n");
remote.sun_family = AF_UNIX;
strcpy(remote.sun_path, SOCK_PATH);
len = strlen(remote.sun_path) + sizeof(remote.sun_family);
if (connect(s, (struct sockaddr*)&remote, len) == -1) {
perror("connect");
exit(1);
}
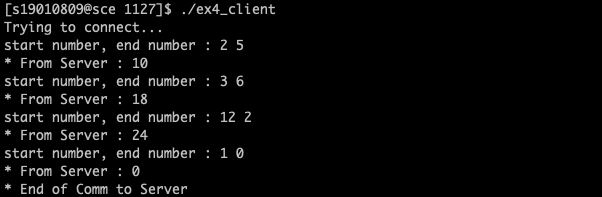
while(1) {
printf("start number, end number : ");
scanf("%d %d", &num[0], &num[1]);
if (send(s, num, sizeof(int)*2, 0) == -1) {
perror("recv");
exit(1);
}
if (recv(s, &ans, sizeof(int), 0) == -1) {
perror("recv");
exit(1);
}
printf("* From Server : %d\n", ans);
if (ans == 0) {
break;
}
}
close(s);
free(num);
printf("* End of Comm to Server\n");
return 0;
}
(ex4_server.c)
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <sys/un.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#define SOCK_PATH "hbsocket"
int main(void) {
int s, s2, t, len, n;
struct sockaddr_un local, remote;
int *num, ans;
num = (int*)malloc(2 * sizeof(int));
if ((s = socket(AF_UNIX, SOCK_STREAM, 0)) == -1) {
perror("socket");
exit(1);
}
local.sun_family = AF_UNIX;
strcpy(local.sun_path, SOCK_PATH);
unlink(local.sun_path);
len = strlen(local.sun_path) + sizeof(local.sun_family);
if (bind(s, (struct sockaddr*)&local, len) == -1) {
perror("bind");
exit(1);
}
if (listen(s, 5) == -1) {
perror("listen");
exit(1);
}
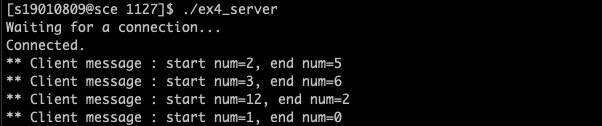
printf("Waiting for a connection...\n");
t = sizeof(remote);
if ((s2 = accept(s, (struct sockaddr*)&remote, &t)) == -1) {
perror("accept");
exit(1);
}
printf("Connected.\n");
while (1) {
if (recv(s2, num, 2 * sizeof(int), 0) == -1) {
perror("recv");
exit(1);
}
printf("** Client message : start num=%d, end num=%d\n", num[0], num[1]);
ans = num[0] * num[1];
if (send(s2, &ans, sizeof(int), 0) == -1) {
perror("send");
exit(1);
}
if (ans == 0) {
break;
}
}
close(s2);
close(s);
free(num);
return 0;
}
참고 및 출처: 시스템 프로그래밍 리눅스&유닉스(이종원)
'Computer Science > UNIX & Linux' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [UNIX/Linux] ep11-3+) TCP 소켓 프로그래밍 실습 (1) | 2024.12.10 |
|---|---|
| [UNIX/Linux] ep11-3) TCP 소켓 프로그래밍 (0) | 2024.12.08 |
| [UNIX/Linux] ep11-2) 소켓 프로그래밍 함수 (0) | 2024.12.04 |
| [UNIX/Linux] ep11-1+) 소켓 프로그래밍 기초 함수 실습 (3) | 2024.12.03 |
| [UNIX/Linux] ep11-1) 소켓 프로그래밍 기초 (4) | 2024.11.26 |



