문제) 크기 M인 해시테이블에 여러 개의 키 값을 입력받아 저장하고, 연쇄법을 이용하여 충돌을 처리하는 해시테이블 프로그램을 작성하시오
[구현 조건]
- 해시테이블은 크기가 M인 배열로 동적 할당한다.
- 입력 키는 중복이 없는 자연수다.
- 키 x에 대한 해시함수 h(x) = x % M 을 사용한다.
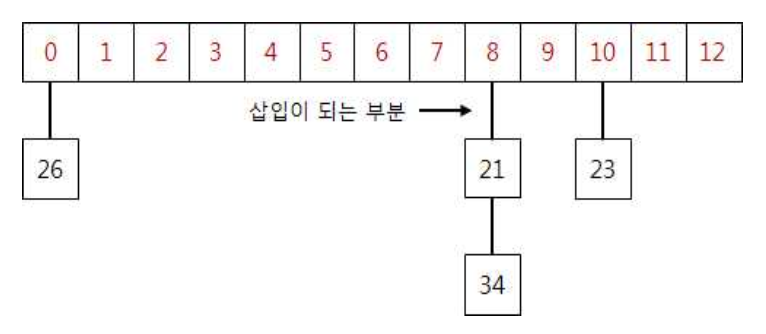
- 삽입 시 충돌이 발생하는 경우, 해당 버켓 리스트의 맨 앞에 삽입한다.
[입력]
- 해시테이블의 크기 M을 입력받는다.
- 삽입(i), 탐색(s), 삭제(d), 인쇄(p) 명령어를 순서에 상관없이 반복하여 입력받는다.
i <x> : 키 x를 해시테이블에 삽입
s <x> : 키 x가 해시테이블에 존재하는지 탐색
d <x> : 키 x가 해시테이블에 존재하면 삭제
p : 해시테이블에 저장된 키들을 순서대로 인쇄(입출력 예시 참조)
e : 프로그램 종료
[출력]
- 키를 삽입하였을 때 아무 출력을 하지 않는다.
- 탐색 또는 삭제할 때, 키가 존재하면 리스트에서 해당 키가 저장된 순위(1부터 시작)를 인쇄하고 없다면 0을 인쇄한다(해시테이블의 주소가 아닌 리스트에서의 순위를 인쇄함에 유의).
- 해시테이블을 인쇄할 때, 0번 주소부터 마지막 주소까지 순회하면서 저장된 키들을 방문하는 순으로 인쇄한다.

(전체코드)
// 분리연쇄법
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
typedef struct NODE {
int key;
struct NODE* next;
} NODE;
NODE** g_hashtable;
int g_M;
void initHashtable();
int hashFunction(int key); // 해시함수
void insertKey(int key);
int searchKey(int key);
int deleteKey(int key);
void printHashtable();
void freeHashtable();
int main() {
char cmd;
int key;
scanf("%d", &g_M);
initHashtable();
while (1) {
scanf(" %c", &cmd);
if (cmd == 'i') {
scanf("%d", &key);
insertKey(key);
}
else if (cmd == 's') {
scanf("%d", &key);
printf("%d\n", searchKey(key));
}
else if (cmd == 'd') {
scanf("%d", &key);
printf("%d\n", deleteKey(key));
}
else if (cmd == 'p') {
printHashtable();
}
else if (cmd == 'e') {
freeHashtable();
return 0;
}
}
}
void initHashtable() {
g_hashtable = (NODE**)malloc(g_M * sizeof(NODE*));
for (int i = 0; i < g_M; i++) {
g_hashtable[i] = NULL; // 모든 해시테이블 버킷을 NULL로 초기화
}
}
// 해시함수
int hashFunction(int key) {
return key % g_M;
}
void insertKey(int key) {
int idx = hashFunction(key); // 해시값을 계산
NODE* newNode = (NODE*)malloc(1 * sizeof(NODE));
newNode->key = key;
newNode->next = g_hashtable[idx]; // 새로운 노드를 현재 버킷의 첫 번째 노드로 설정
g_hashtable[idx] = newNode; // 해시 테이블 버킷 갱신
}
int searchKey(int key) {
int idx = hashFunction(key); // 해시값을 계산
NODE* target = g_hashtable[idx];
int position = 1;
while (target != NULL) {
if (target->key == key) {
return position;
}
target = target->next;
position++;
}
return 0;
}
int deleteKey(int key) {
int idx = hashFunction(key); // 해시값을 계산
NODE* prev = NULL;
NODE* target = g_hashtable[idx];
int position = 1;
while (target != NULL && target->key != key) {
prev = target;
target = target->next;
position++;
}
if (target == NULL) {
return 0;
}
if (prev == NULL) { // 삭제할 노드가 첫 번째 노드인 경우
g_hashtable[idx] = target->next; // 버킷의 첫 번째 노드를 다음 노드로 설정
}
else { // 삭제할 노드가 중간에 있는 경우
prev->next = target->next; // 이전 노드의 다음 노드를 현재 노드의 다음 노드로 설정
}
free(target);
return position;
}
void printHashtable() {
for (int i = 0; i < g_M; i++) {
NODE* cur = g_hashtable[i];
while (cur != NULL) {
printf(" %d", cur->key);
cur = cur->next;
}
}
printf("\n");
}
void freeHashtable() {
for (int i = 0; i < g_M; i++) {
NODE* cur = g_hashtable[i];
while (cur != NULL) {
NODE* temp = cur;
cur = cur->next;
free(temp);
}
}
free(g_hashtable);
}
/*
13
i 34
i 23
i 26
i 21
s 36
*/
출처 및 참고: 알고리즘-원리와 응용(국형준교수님), Algorithm Design(Jon Kleinberg, Eva Tardos), Foundations of Algorithms using C++(Richard Neapolitan)
'Computer Science > 알고리즘' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [알고리즘] ep4+++) 비활성화 방식 삭제 (0) | 2024.07.19 |
|---|---|
| [알고리즘] ep4++) 개방주소법 구현(선형 조사, 이중 해싱) (3) | 2024.07.19 |
| [알고리즘] ep4) 해시테이블(hashtable) (0) | 2024.07.18 |
| [알고리즘] ep3++) AVL 트리 구현 (0) | 2024.07.17 |
| [알고리즘] ep3+) 이진탐색트리(BST) 구현 (0) | 2024.07.17 |



